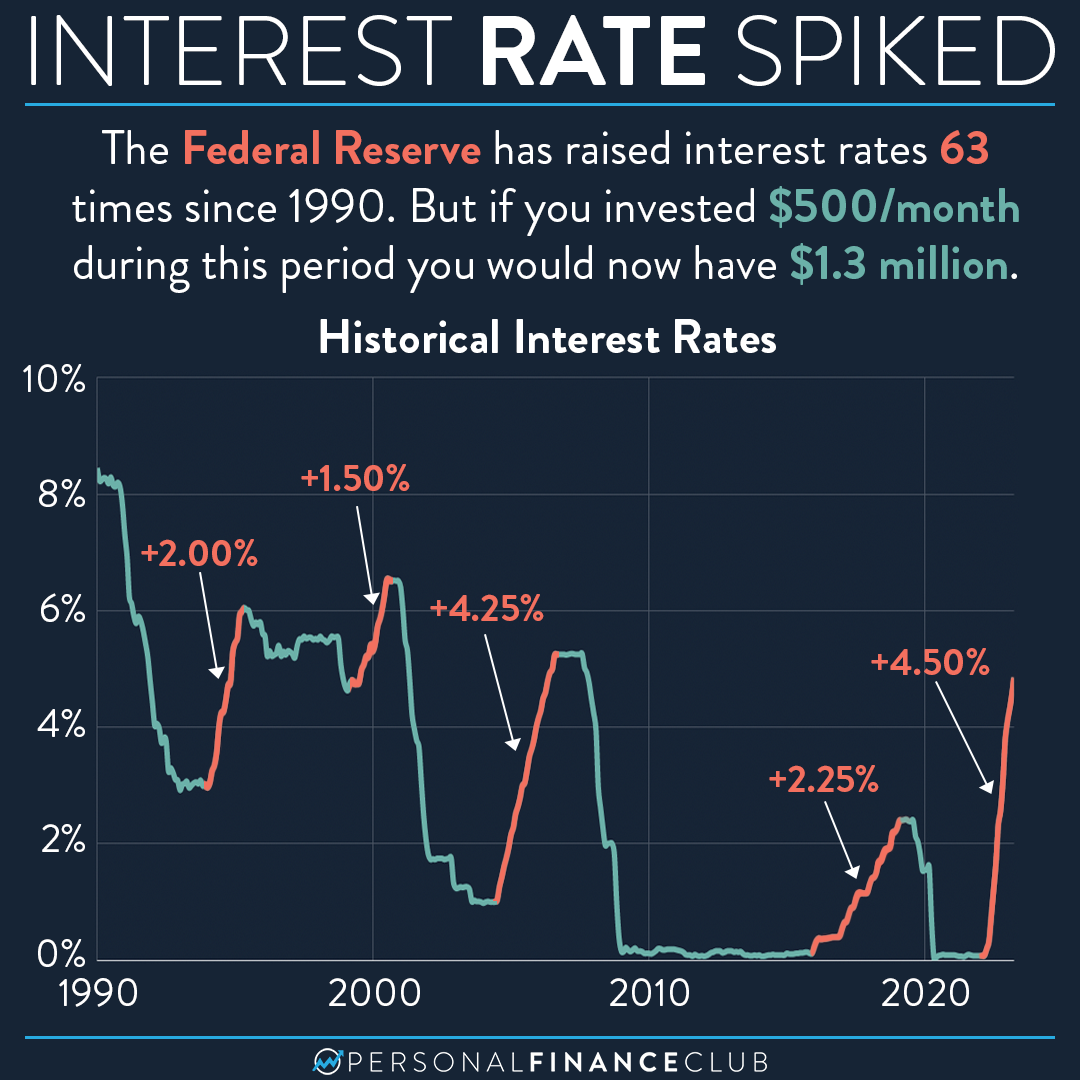
The Federal Reserve interest rates play a pivotal role in shaping the U.S. economy and global financial markets. As one of the most influential monetary policy tools, these rates affect everything from consumer borrowing to investment decisions. Whether you're an investor, a business owner, or an everyday consumer, understanding how the Federal Reserve sets interest rates is crucial to navigating the economic landscape.
For decades, the Federal Reserve has been tasked with managing monetary policy to ensure economic stability. By adjusting interest rates, the central bank influences inflation, employment levels, and overall economic growth. This article dives deep into the mechanics of how the Federal Reserve interest rates work, their impact on the economy, and why they matter to you.
Whether you're new to the concept of interest rates or seeking advanced insights into the Federal Reserve's decision-making process, this guide will provide you with the knowledge you need. From historical context to future projections, we'll cover everything you need to know about federal reserve interest rates.
Read also:Hazem Robux Net Worth Unveiling The Wealth Of The Roblox Entrepreneur
Table of Contents
- Overview of Federal Reserve Interest Rates
- The Federal Reserve's Role in Setting Interest Rates
- How the Federal Reserve Adjusts Interest Rates
- The Impact of Federal Reserve Interest Rates on the Economy
- Factors That Influence Federal Reserve Interest Rates
- A Historical Perspective on Federal Reserve Interest Rates
- Current Trends in Federal Reserve Interest Rates
- Future Projections for Federal Reserve Interest Rates
- Global Effects of Federal Reserve Interest Rates
- Conclusion and Call to Action
Overview of Federal Reserve Interest Rates
The federal reserve interest rates refer to the target range set by the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC), which is a key component of the Federal Reserve System. This rate influences short-term interest rates throughout the economy, impacting borrowing costs for consumers and businesses alike. It serves as a benchmark for various financial instruments, including mortgages, credit cards, and loans.
Understanding the federal reserve interest rates requires an appreciation of the dual mandate of the Federal Reserve: promoting maximum employment and maintaining price stability. By adjusting these rates, the Federal Reserve aims to achieve its goals while balancing the risks of inflation and economic downturns.
For example, during periods of economic growth, the Federal Reserve may raise interest rates to prevent overheating and control inflation. Conversely, during recessions, it may lower rates to stimulate borrowing and spending, thereby boosting economic activity.
The Federal Reserve's Role in Setting Interest Rates
What Is the Federal Reserve?
The Federal Reserve, often referred to as the "Fed," is the central banking system of the United States. Established in 1913, its primary responsibilities include conducting monetary policy, supervising and regulating banks, maintaining financial stability, and providing financial services to the U.S. government.
How Does the Federal Reserve Influence Rates?
Through the FOMC, the Federal Reserve sets a target range for the federal funds rate, which is the interest rate at which banks lend reserve balances to one another overnight. This rate serves as the foundation for other interest rates in the economy. The Federal Reserve uses open market operations, adjusting the money supply, and setting reserve requirements to influence this rate.
By controlling the federal funds rate, the Federal Reserve can influence broader economic conditions. For instance, lowering the rate makes borrowing cheaper, encouraging businesses to invest and consumers to spend. Conversely, raising the rate makes borrowing more expensive, which can help curb inflation.
Read also:Ds Emulator For Ios The Ultimate Guide To Playing Nintendo Ds Games On Your Iphone
How the Federal Reserve Adjusts Interest Rates
The Federal Reserve employs several tools to adjust interest rates. These include:
- Open Market Operations (OMO): The Federal Reserve buys or sells government securities to influence the money supply. Purchasing securities injects money into the economy, lowering interest rates, while selling securities reduces liquidity, raising rates.
- Reserve Requirements: The Federal Reserve sets the minimum amount of reserves that banks must hold. By altering these requirements, it can influence the availability of credit in the economy.
- Discount Rate: This is the interest rate charged to commercial banks and other depository institutions on loans they receive from the Federal Reserve's discount window. Adjusting the discount rate can influence borrowing costs for banks.
These tools work in tandem to achieve the desired federal reserve interest rates and influence economic conditions.
The Impact of Federal Reserve Interest Rates on the Economy
Effects on Consumers
Changes in federal reserve interest rates directly affect consumers. Lower rates make borrowing cheaper, encouraging spending on big-ticket items like homes and cars. Higher rates, on the other hand, increase the cost of borrowing, potentially reducing consumer spending.
Effects on Businesses
Businesses are also significantly impacted by federal reserve interest rates. Lower rates can reduce the cost of capital, encouraging investment in new projects and expansion. Conversely, higher rates may lead businesses to tighten their belts, reducing capital expenditures and hiring.
For instance, during the 2008 financial crisis, the Federal Reserve slashed interest rates to near-zero levels to stimulate economic recovery. This move helped stabilize the economy and restore confidence among consumers and businesses.
Factors That Influence Federal Reserve Interest Rates
Several factors influence the Federal Reserve's decision-making process regarding interest rates:
- Inflation: The Federal Reserve closely monitors inflation levels. If inflation rises above its target rate of 2%, it may raise interest rates to cool down the economy.
- Economic Growth: Strong economic growth may lead to higher interest rates to prevent overheating, while weak growth may prompt rate cuts to stimulate activity.
- Unemployment: The Federal Reserve considers employment levels when setting interest rates. High unemployment may lead to lower rates to encourage job creation.
- Global Economic Conditions: The Federal Reserve also takes into account global economic trends, as they can impact the U.S. economy and financial markets.
By analyzing these factors, the Federal Reserve makes informed decisions about the appropriate level of federal reserve interest rates.
A Historical Perspective on Federal Reserve Interest Rates
Throughout history, the Federal Reserve has adjusted interest rates in response to various economic challenges. For example, during the 1970s, high inflation prompted the Federal Reserve to raise rates significantly, leading to a recession but ultimately bringing inflation under control.
In contrast, the 2008 financial crisis saw the Federal Reserve lower rates to near-zero levels to stabilize the economy. This period marked one of the longest stretches of low federal reserve interest rates in history.
By examining these historical trends, we can better understand the Federal Reserve's approach to managing interest rates and its impact on the economy.
Current Trends in Federal Reserve Interest Rates
As of the latest FOMC meeting, the Federal Reserve has maintained a cautious stance on interest rates. With inflation showing signs of moderation and the labor market remaining strong, the Federal Reserve has signaled that it may keep rates steady for the foreseeable future.
However, economic uncertainties, such as geopolitical tensions and potential supply chain disruptions, could influence future decisions. The Federal Reserve remains vigilant, ready to adjust federal reserve interest rates as needed to ensure economic stability.
Future Projections for Federal Reserve Interest Rates
Looking ahead, economists project that federal reserve interest rates will remain relatively stable unless significant changes occur in economic conditions. However, the Federal Reserve has emphasized its commitment to data-driven decision-making, meaning future rate adjustments will depend on evolving economic indicators.
Investors and businesses should monitor key economic data, such as inflation reports and employment figures, to anticipate potential changes in federal reserve interest rates. Staying informed can help them make better financial decisions.
Global Effects of Federal Reserve Interest Rates
The Federal Reserve's decisions on interest rates have far-reaching effects beyond U.S. borders. As the world's largest economy, changes in federal reserve interest rates can influence global financial markets, currency exchange rates, and capital flows.
For instance, higher U.S. interest rates can attract foreign capital, strengthening the dollar and potentially impacting emerging markets. Conversely, lower rates may lead to capital outflows, weakening the dollar and affecting global trade dynamics.
By considering these global effects, the Federal Reserve ensures its policies align with broader international economic stability.
Conclusion and Call to Action
In conclusion, federal reserve interest rates are a critical component of monetary policy, influencing economic conditions both domestically and globally. Understanding how the Federal Reserve sets these rates and their impact on the economy is essential for anyone seeking to navigate the financial landscape effectively.
We encourage you to engage with this content by leaving your thoughts in the comments section below. Share this article with others who may find it informative, and explore more resources on our site to deepen your knowledge of economics and finance.
Stay informed, stay proactive, and let's work together to build a more financially literate community!