Segregation ban has become a pivotal topic in discussions surrounding human rights, equality, and social justice. It addresses the critical need to dismantle discriminatory practices that separate individuals based on race, ethnicity, religion, or other identifying factors. As societies evolve, understanding the implications and history of segregation bans is essential for fostering inclusive communities.
The concept of segregation ban is rooted in the struggle for equality and civil rights. Historically, segregation was enforced through laws and societal norms that perpetuated inequality. Today, the fight against segregation continues, with governments and organizations implementing policies to ensure equal opportunities for all individuals.
This article delves into the intricacies of segregation bans, exploring their historical context, legal implications, societal impact, and the ongoing efforts to combat segregation in modern times. By understanding the challenges and successes of segregation bans, we can work towards a more equitable world.
Read also:Savannah Guthrie Today Show A Closer Look At Her Journey And Impact
Table of Contents
- History of Segregation Ban
- Legal Framework of Segregation Ban
- Social Impact of Segregation Ban
- Economic Effects of Segregation Ban
- Segregation Ban in Education
- Segregation Ban in Housing
- Challenges in Implementing Segregation Ban
- Global Perspective on Segregation Ban
- Future Directions for Segregation Ban
- Conclusion
History of Segregation Ban
Segregation has a long and tumultuous history, with its roots tracing back to colonial times. In the United States, segregation was legally enforced through Jim Crow laws, which mandated racial separation in public facilities. The Civil Rights Movement of the 1950s and 1960s played a crucial role in challenging these discriminatory practices, leading to landmark legislation such as the Civil Rights Act of 1964.
In South Africa, apartheid was a system of institutionalized racial segregation and discrimination enforced by the government from 1948 until the early 1990s. The global outcry against apartheid led to international sanctions and pressure, eventually resulting in its dismantling.
Key events in the history of segregation bans include:
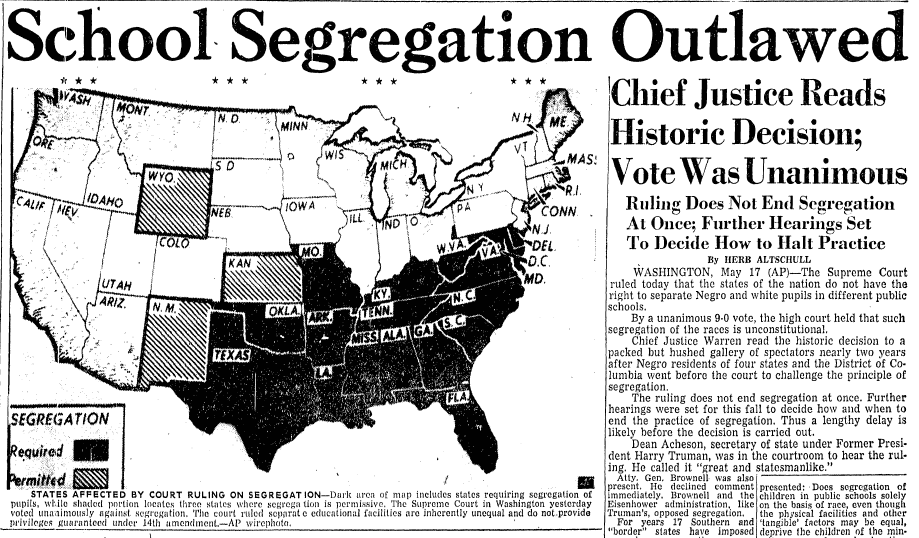
- Brown v. Board of Education (1954): A U.S. Supreme Court decision that declared state laws establishing separate public schools for black and white students unconstitutional.
- Civil Rights Act of 1964: A landmark law that prohibited discrimination based on race, color, religion, sex, or national origin.
- End of Apartheid in South Africa (1994): The election of Nelson Mandela as the first black president marked the end of apartheid.
Impact of Historical Segregation
The legacy of historical segregation continues to affect societies today. Systemic inequalities persist in areas such as education, employment, and housing. Understanding the historical context of segregation bans is vital for addressing these ongoing challenges.
Legal Framework of Segregation Ban
The legal framework surrounding segregation bans varies across countries and regions. In the United States, the Constitution and federal laws provide protections against discrimination. The Equal Protection Clause of the Fourteenth Amendment ensures that no state shall deny any person within its jurisdiction "the equal protection of the laws."
Internationally, human rights treaties such as the International Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Racial Discrimination (ICERD) aim to eliminate racial discrimination and promote equality. These legal instruments provide a foundation for challenging segregation and promoting inclusivity.
Read also:23 May Star Sign Unveiling The Zodiac Secrets Of Gemini
Key legal principles include:
- Equal Protection Clause
- International human rights treaties
- Anti-discrimination laws
Enforcement of Segregation Bans
Enforcing segregation bans requires robust legal mechanisms and oversight. Governments and organizations must ensure compliance with anti-discrimination laws and address violations through appropriate legal channels. Education and awareness campaigns also play a crucial role in promoting understanding and compliance with segregation bans.
Social Impact of Segregation Ban
The social impact of segregation bans is profound, affecting communities and individuals in various ways. By dismantling segregation, societies can foster greater understanding and cooperation among diverse groups. However, the process of implementing segregation bans often encounters resistance and challenges.
Research indicates that integrated communities experience improved social cohesion and reduced prejudice. For example, a study by the National Bureau of Economic Research found that desegregating schools led to better academic outcomes and reduced racial bias among students.
Key social benefits of segregation bans include:
- Improved social cohesion
- Reduced prejudice and discrimination
- Enhanced opportunities for marginalized groups
Community Responses to Segregation Ban
Community responses to segregation bans vary widely, depending on cultural, historical, and political contexts. While some communities embrace integration and equality, others may resist changes to traditional practices. Engaging communities in dialogue and education is essential for fostering acceptance and understanding of segregation bans.
Economic Effects of Segregation Ban
Segregation bans have significant economic implications, impacting labor markets, housing, and business opportunities. By promoting equality and inclusivity, segregation bans can enhance economic productivity and reduce disparities.
Studies show that integrated workplaces and communities experience increased innovation and creativity. For example, a report by McKinsey & Company found that companies with diverse leadership teams are 33% more likely to outperform their peers.
Key economic benefits of segregation bans include:
- Increased economic productivity
- Reduced disparities in income and employment
- Enhanced business opportunities for underrepresented groups
Addressing Economic Disparities
Addressing economic disparities requires a multi-faceted approach, including policy reforms, education, and economic empowerment programs. Governments and organizations must work together to ensure that all individuals have access to opportunities and resources, regardless of their background.
Segregation Ban in Education
Education is a critical area where segregation bans have made significant strides. The integration of schools has been a focal point of civil rights movements worldwide. However, challenges such as funding disparities and systemic inequalities persist in many educational systems.
Research indicates that integrated schools provide better educational outcomes for students from diverse backgrounds. For example, a study by the Century Foundation found that students in racially and economically integrated schools perform better academically and are more likely to attend college.
Key strategies for promoting integration in education include:
- Implementing school choice programs
- Addressing funding disparities
- Promoting diversity in teaching staff
Challenges in Educational Integration
Despite progress, challenges remain in achieving full integration in education. Issues such as residential segregation, resource allocation, and cultural biases can hinder efforts to promote equality in schools. Addressing these challenges requires a collaborative effort from educators, policymakers, and communities.
Segregation Ban in Housing
Housing is another critical area where segregation bans have been implemented. The Fair Housing Act of 1968 in the United States prohibited discrimination in the sale, rental, and financing of housing based on race, color, religion, or national origin. However, residential segregation persists in many communities due to historical and systemic factors.
Research shows that integrated neighborhoods provide better access to resources and opportunities for residents. For example, a study by the Urban Institute found that living in a low-poverty neighborhood improves educational and economic outcomes for children.
Key strategies for promoting housing integration include:
- Implementing affordable housing programs
- Addressing zoning laws and regulations
- Promoting diversity in neighborhood development
Addressing Residential Segregation
Addressing residential segregation requires addressing historical injustices and systemic inequalities. Governments and organizations must work together to create policies and programs that promote fair housing and equal opportunities for all individuals.
Challenges in Implementing Segregation Ban
Implementing segregation bans is not without challenges. Resistance from certain groups, lack of resources, and systemic inequalities can hinder progress. Overcoming these challenges requires a comprehensive approach that addresses the root causes of segregation.
Key challenges in implementing segregation bans include:
- Resistance from traditionalists and segregationists
- Limited resources for enforcement and education
- Persistent systemic inequalities
Strategies for Overcoming Challenges
Strategies for overcoming challenges in implementing segregation bans include education, policy reform, and community engagement. By fostering understanding and cooperation among diverse groups, societies can work towards a more inclusive future.
Global Perspective on Segregation Ban
The global perspective on segregation bans highlights the universal need for equality and human rights. While progress has been made in many countries, challenges persist in addressing systemic inequalities and promoting integration.
International organizations such as the United Nations play a crucial role in promoting segregation bans and addressing human rights violations. By working together, nations can create a more equitable world for all individuals.
Key global initiatives include:
- International Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Racial Discrimination (ICERD)
- United Nations Human Rights Council
- Regional human rights treaties
Comparative Analysis of Segregation Bans
A comparative analysis of segregation bans across countries reveals both successes and challenges. While some nations have made significant progress in promoting equality, others continue to struggle with systemic inequalities and discrimination. Understanding these differences is essential for developing effective strategies to combat segregation.
Future Directions for Segregation Ban
The future of segregation bans lies in continued efforts to promote equality and inclusivity. By addressing systemic inequalities and fostering understanding among diverse groups, societies can work towards a more equitable future.
Key future directions for segregation bans include:
- Strengthening legal frameworks and enforcement mechanisms
- Promoting education and awareness campaigns
- Addressing economic and social disparities
Innovative Approaches to Segregation Ban
Innovative approaches to segregation bans include technology, community engagement, and policy reform. By leveraging these tools, societies can create more effective strategies for promoting equality and inclusivity.
Conclusion
In conclusion, segregation bans play a crucial role in promoting equality and human rights. By understanding their historical context, legal framework, and societal impact, we can work towards a more inclusive future. The challenges of implementing segregation bans require a comprehensive approach that addresses systemic inequalities and fosters understanding among diverse groups.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences in the comments section below. Your feedback is valuable in promoting dialogue and understanding on this critical topic. Additionally, explore other articles on our website to learn more about related issues and contribute to the conversation.